EU mandates replaceable phone batteries: Here’s what you need to know
European Union is known for its stringent laws that aim to protect consumer rights and the environment. One such recent mandate passed by the EU requires future smartphones, tablets, e-readers, and other portable electronic devices to sport user-replaceable batteries to help combat the problem of e-waste. Here’s everything you need to know about the EU’s new battery regulation:
What the new regulation entails

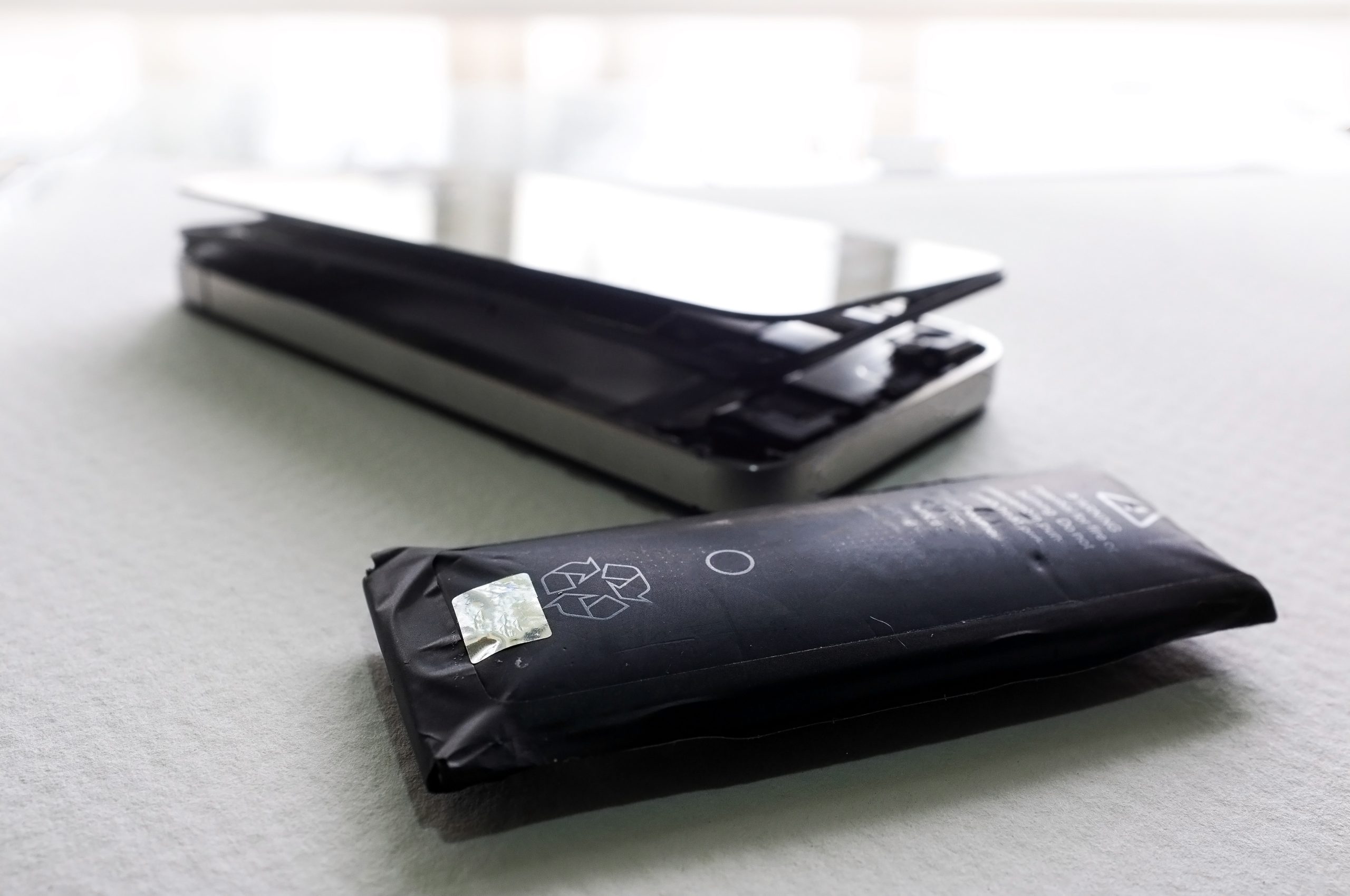
The new regulation requires manufacturers to make the necessary changes to ensure their devices have user-replaceable batteries. The rules cover batteries of all sizes, including portable batteries, SLI batteries for vehicles, LMT batteries for scooters and e-bikes, EV batteries, and industrial batteries.
Labeling the batteries
Batteries across the board should have labels and QR codes containing capacity, performance, durability, chemical composition, and a “separate collection” symbol. Moreover, every battery will have digital passports with details on the general battery model, along with the individual battery.
Collection of old batteries
The plan mandates that manufacturers collect old batteries and establish minimum levels of recycled materials for batteries.
Portable batteries
The EU requires that out of the total portable batteries available on the market, at least 45% of them should be collected for recycling by 2023, 63% by 2027, and 73% by 2030.
LMT batteries
The numbers are 51% by 2028 and 61% by 2031.
Other batteries
Every other battery, including EV and industrial, must be recycled at no cost to the consumer, irrespective of their condition, origin, or brand.
Retailer Program
Manufacturers selling devices in the EU must develop a due diligence strategy to tackle social and environmental risks linked to sourcing and trading raw materials and secondary raw materials.
How does the new regulation benefit the environment?

The restriction will aid in developing the EU recycling industry, particularly for lithium, and establish a competitive industrial sector. The purpose of the regulation is to promote a circular economy and reduce e-waste occurrences. Recycled-material requirements aim to ensure 16% cobalt, 85% lead, 6% lithium, and 6% nickel per battery.
How to adapt to the new regulation?

Manufacturers must focus on their design and production process, ensuring that their future devices have easily removable batteries. With the regulation now set in place, the industry has approximately 3.5 years to make it a possibility.
Conclusion

The new EU regulation adds another layer of protection for consumer rights and promotes environmental sustainability. The aim is to combat the e-waste problem while improving people’s safety when handling batteries. The directive, along with other initiatives, undoubtedly puts the EU at the forefront of the green technology and recycling industry.
FAQs
1. What is the aim of the new battery regulation?
The EU’s new battery regulation aims to tackle the e-waste problem while improving user safety and promoting environmental sustainability.
2. When will the new regulation come into effect?
The new battery regulation will come into effect from the end of 2024.
3. What types of batteries does the regulation cover?
The regulation covers every battery size, including portable batteries, SLI batteries for vehicles, LMT batteries for scooters and e-bikes, EV batteries, and industrial batteries.
4. What do the battery labels and QR codes contain?
Battery labels and QR codes contain capacity, performance, durability, chemical composition, and a “separate collection” symbol with the digital passports displaying the general battery model and individual battery.
5. What percentage of old portable batteries must be collected for recycling by 2030?
The plan mandates that out of the total portable batteries, 73% should be collected for recycling by 2030.

