## From Lab Coat to Lobbyist: Pace’s Ben McDonald is Bridging Science and Policy for a Healthier Planet
Picture this: a scientist armed not just with a pipette and a microscope, but with the knowledge of policy and the drive to enact real-world change. That’s Ben McDonald ’25, a Pace University student who’s on a mission to create a healthier environment.
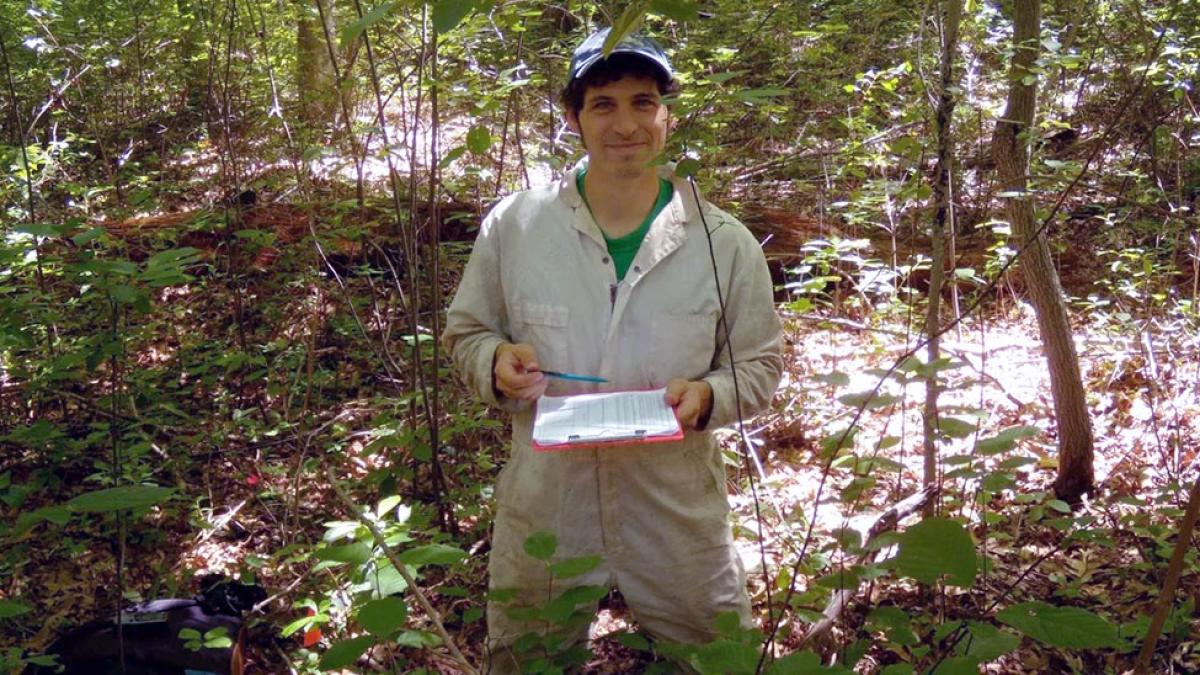

Forget the ivory tower – Ben is blending the rigor of scientific research with the power of policy to tackle some of the world’s most pressing environmental challenges. His story is a testament to the power of interdisciplinary thinking, showing us how one individual can make a tangible impact on the world around us.

The Influence of Environmental Science and Policy on Health Care
The intersection between environmental science and health care is critical for improving public health outcomes. Environmental factors such as air and water quality, exposure to toxins, and urban planning all play significant roles in affecting health care delivery and community well-being. Effective policies can promote a healthier environment by setting standards, guiding regulations, and facilitating community engagement. Environmental scientists can contribute to health care improvements by providing evidence-based data and solutions that help mitigate environmental risks and enhance public health.

Environmental Factors Affecting Health Care Delivery
Environmental factors like pollution, climate change, and natural disasters can directly impact health care services. For example, air pollution can exacerbate respiratory issues, leading to increased hospital admissions and higher health care costs. Similarly, extreme weather conditions can disrupt medical facilities and supply chains, affecting the delivery of health services.

The Role of Policy in Promoting a Healthier Environment
Policy plays a critical role in promoting a healthier environment. Legislation and regulations can mandate reductions in pollution, enforce safety standards in industries, and promote sustainable practices. Policies like the Clean Air Act in the U.S. have significantly reduced air pollution levels, leading to better respiratory health and fewer hospitalizations. By integrating environmental science with policy, health care professionals can work towards creating healthier communities and reducing the burden on health care systems.

Potential for Environmental Scientists to Contribute to Health Care Improvements
Environmental scientists can contribute to health care improvements by providing evidence-based recommendations for policy makers and health care professionals. For example, studies on the impact of air and water quality on public health can inform policy decisions, leading to better health outcomes. Environmental scientists can also develop models and tools to predict and mitigate environmental risks, aiding in the design of more effective public health interventions.

Practical Applications in Health Care Settings
The practical applications of environmental science and policy in health care settings are vast and varied. These applications range from improving indoor air quality in hospitals to reducing the environmental impact of health care operations.

Examples of Environmental Policy Impacting Health Care
- Indoor Air Quality: Policies that mandate the use of green building materials and energy-efficient HVAC systems can significantly improve indoor air quality, reducing the incidence of respiratory infections among patients and staff.
- Waste Management: Hospitals are major producers of medical waste. Policies aimed at reducing waste, such as recycling programs and hazardous waste management protocols, can minimize the environmental footprint of health care facilities while also reducing costs.
- Water Quality: Ensuring safe and sustainable water supplies is essential for both patient care and the general public. Policies and guidelines that maintain high standards of water purity can prevent waterborne diseases and protect patients from harmful contaminants.
- Case Study 1: Kaiser Permanente’s Green Hospitals: Kaiser Permanente has implemented green building practices in several of its hospitals, resulting in energy savings, improved air quality, and reduced waste. These improvements have not only enhanced patient and staff health but also reduced operational costs.
- Case Study 2: Cleveland Clinic’s Sustainable Operations: Cleveland Clinic has adopted sustainable practices, such as recycling and waste reduction, which have led to the reduction of medical waste and a decrease in hospital-acquired infections.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration between environmental scientists, health care professionals, and policy makers to develop more effective and sustainable health care practices.
- Technology Integration: Leveraging technology to monitor and manage environmental conditions in real-time, ensuring that health care facilities maintain optimal conditions for patient care and staff well-being.
- Community Engagement: Engaging communities in environmental health initiatives, promoting public health through education, and involving community members in policy development and implementation.
Case Studies of Successful Environmental Interventions in Health Care
Several health care facilities have successfully implemented environmental interventions that have led to improved health outcomes and operational efficiencies.
Future Directions for Integrating Environmental Science and Policy in Health Care
Future directions for integrating environmental science and policy in health care settings will involve more comprehensive approaches to patient care and facility management. This includes:
Implications for Health Care Professionals
The integration of environmental science and policy into health care has significant implications for health care professionals. This integration requires a multidisciplinary approach, bolstered by specialized training and education in environmental science and policy.
The Importance of a Multidisciplinary Approach
A multidisciplinary approach is essential for addressing the complex environmental factors that influence health. Health care professionals, environmental scientists, and policy makers must work together to identify environmental risks and develop evidence-based interventions. This collaboration can lead to more effective health care practices and improved patient outcomes.
Training and Education in Environmental Science and Policy for Health Care Professionals
Health care professionals need to be educated on the principles of environmental science and policy to effectively address environmental health challenges. Training programs can include:
- Environmental Health Courses: Courses focused on environmental health and policy can help health care professionals understand the environmental determinants of health.
- Interdisciplinary Workshops: Workshops that bring together health care professionals, environmental scientists, and policy makers can foster collaboration and sharing of expertise.
- Continuing Education: Continuous learning opportunities can help professionals stay updated on the latest environmental science and policy trends and their implications for health care.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: By reducing environmental risks, patients can experience fewer health problems, leading to better overall health and well-being.
- Cost Savings: Effective environmental management can reduce health care costs by preventing environmentally-induced illnesses and reducing the burden on the health care system.
- Enhanced Community Health: Healthier environments can lead to healthier communities, reducing the overall need for health care services and promoting a healthier population.
Long-Term Benefits for Patients and the Health Care System
The long-term benefits of integrating environmental science and policy into health care are substantial. These benefits include:
Saugus Union School District: A Model of Excellence
The Saugus Union School District (SUSD) exemplifies excellence in elementary education by focusing on the whole child and creating positive, inclusive learning environments. This section explores the district’s core values, achievements, and commitment to continuous improvement.
Core Values and Whole Child Approach
SUSD emphasizes core values such as respect, integrity, and lifelong learning to foster a supportive and inclusive educational environment. The district’s whole child approach integrates social-emotional learning with academic learning, ensuring that each child’s needs are addressed comprehensively.
Achievements and Recognition
SUSD has achieved significant recognition for its efforts in promoting a healthy and positive learning environment. The district’s recognition by the Alliance for a Healthier Generation and its achievements in Positive Behavior Intervention Supports (PBIS) demonstrate its commitment to the well-being of its students.
- Award of Excellence: SUSD has been identified as one of America’s Healthiest Schools, highlighting its efforts in creating a healthy school environment.
- PBIS Recognition: SUSD’s sites have received platinum, gold, and silver awards for their site-specific PBIS work, indicating a high level of commitment to behavioral health and student success.
- Model PLC Schools: Schools like Charles Helmers Elementary and West Creek Academy have been recognized as model Professional Learning Communities (PLCs), showcasing the district’s commitment to collaborative and continuous learning.
Community and Continuous Improvement
SUSD’s dedication to continuous improvement is evident in its commitment to the “whole child” philosophy. The district’s collaborative approach, encompassing classified staff, teachers, and administrators, ensures that each school site is tailored to meet the needs of its students. By using data and standards to drive instruction, SUSD aims to enhance academic achievement and foster a positive learning environment.
Future Prospects and Career Goals
Ben McDonald, a graduate student pursuing a Master of Science in Environmental Science and Policy at Pace University, is well-positioned to contribute to the field of environmental health. His career aspirations and experiences provide a glimpse into the future of environmental science and policy.
Ben McDonald’s Career Aspirations
Ben McDonald’s career goals include exploring policy advocacy and habitat restoration. His experiences as a research assistant at Riverkeeper and intern at Waterfront Alliance have equipped him with valuable skills and connections in the field. These experiences have not only honed his academic knowledge but also provided practical insights into environmental challenges and the need for effective policy solutions. Ben aims to leverage these skills to advocate for and implement policies that enhance environmental health and sustainability.
The Future of Environmental Science and Policy
The future of environmental science and policy is poised to address emerging challenges such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and sustainable development. Advances in technology and data analytics will play a crucial role in this field, enabling more precise and effective environmental management and policy-making.
Inspirations and Advice for Aspiring Environmental Scientists
Ben McDonald’s journey offers valuable lessons for aspiring environmental scientists. He emphasizes the importance of mentorship and hands-on experience. Engaging with experienced professionals and participating in practical projects can provide the practical knowledge and skills necessary to make a meaningful impact. Aspiring environmental scientists should seek out opportunities for mentorship, engage in interdisciplinary collaborations, and stay informed about the latest research and policy developments.
Conclusion
A Perfect Blend of Science and Policy: Ben McDonald ’25 Ready to Create a Healthier Environment
In “A perfect blend of science and policy: Ben McDonald ’25 is ready to create a healthier environment – Pace News,” Ben McDonald ’25 showcased his remarkable journey, highlighting the crucial role of science and policy in addressing complex environmental issues. McDonald, a rising environmental leader, demonstrated his expertise in bridging the gap between cutting-edge scientific research and effective policy-making.
McDonald’s work emphasizes the significance of understanding the interconnectedness of environmental, social, and economic factors. He illustrated this point by emphasizing the need for policymakers to consider the long-term consequences of their decisions and the impact on future generations. This perspective is particularly relevant in the face of growing challenges, such as climate change, which demands a holistic approach.
As McDonald continues to navigate the intricate landscape of environmental policy, his message serves as a powerful call to action. He encourages policymakers to prioritize science-driven solutions, empowering them to create a healthier environment that balances people’s needs with the well-being of the planet. By embracing this fusion of science and policy, we can unlock a brighter future, where sustainability and prosperity are inextricably linked.
As we approach the future, it is essential that we remain committed to the principles of scientific inquiry and policy-making that have enabled Ben McDonald ’25 to make a meaningful impact. By harnessing the power of these two disciplines, we can create a more sustainable and equitable world for all. As McDonald aptly put it, “The future is not a destination, but a journey of discovery, and it’s up to us to chart a course that benefits both people and the planet.”
